 Clicking on an atom produces an identification
report in the Jmol rectangle, to the lower left of the molecule (see
snapshot at right), and also in the browser's status bar.
Amino acids are reported as
3-letter abbreviations,
and nucleotides as
Clicking on an atom produces an identification
report in the Jmol rectangle, to the lower left of the molecule (see
snapshot at right), and also in the browser's status bar.
Amino acids are reported as
3-letter abbreviations,
and nucleotides as
A, DA, C, DC, G, DG, T, DT, U, or DU (D for Deoxy).
Ligands and non-standard residues have other abbreviations.
Atoms are identified using PDB file format nomenclature, as follows:
|
CA = Carbon, Alpha (1st) CB = Carbon, Beta (2nd) CG, OG = Carbon/Oxygen, Gamma (3rd) CD = Carbon, Delta (4th) CE, NE, OE = Carbon/Nitrogen/Oxygen, Epsilon (5th) NZ = Nitrogen, Zeta (6th) NH = Nitrogen, Eta (7th) |
O3', O5' = 3' and 5' pentose oxygens C1' to C5' = 1' to 5' pentose carbons C2-C8, N1-N9, O2-O6 = elements in bases C5M = C5 Methyl (in Thymine) |
 In addition to clicking, you can simply touch an atom with the mouse
(without moving the mouse, which is called "hovering"), and after a
delay of about two seconds, a yellow message will appear near the
mouse pointer (see snapshot at right) with an atom identification
report. This works best with Spin off.
In addition to clicking, you can simply touch an atom with the mouse
(without moving the mouse, which is called "hovering"), and after a
delay of about two seconds, a yellow message will appear near the
mouse pointer (see snapshot at right) with an atom identification
report. This works best with Spin off.
To visualize a cavity:
- Use the Solid view.
- Turn on the Slab button.
- In the lower Slab help panel, check "Don't hide the back of the molecule".
Examples: 3hyc has a cavity. 7ahl and 1mxm have channels.
Most molecules will have none of these labels when displayed in FirstGlance in Jmol. Some molecules will have one or more of these kinds of labels.
- X marks non-standard residues.
- S- marks incomplete Sidechains.
- ? marks anomalous atoms.
 These labels or marks are shown by default, but can be hidden by
unchecking the checkbox Labels: Show at the bottom of any
of the upper left panels. (You may have to scroll the upper left panel
down to see this checkbox.)
These labels or marks are shown by default, but can be hidden by
unchecking the checkbox Labels: Show at the bottom of any
of the upper left panels. (You may have to scroll the upper left panel
down to see this checkbox.)
By default, labels behind other atoms are hidden. To make sure you can see all labels, check the checkbox Labels: Front at the bottom of any of the upper left panels.
Check ID to add identifications to the labels for all atoms marked X, S-, or ?.
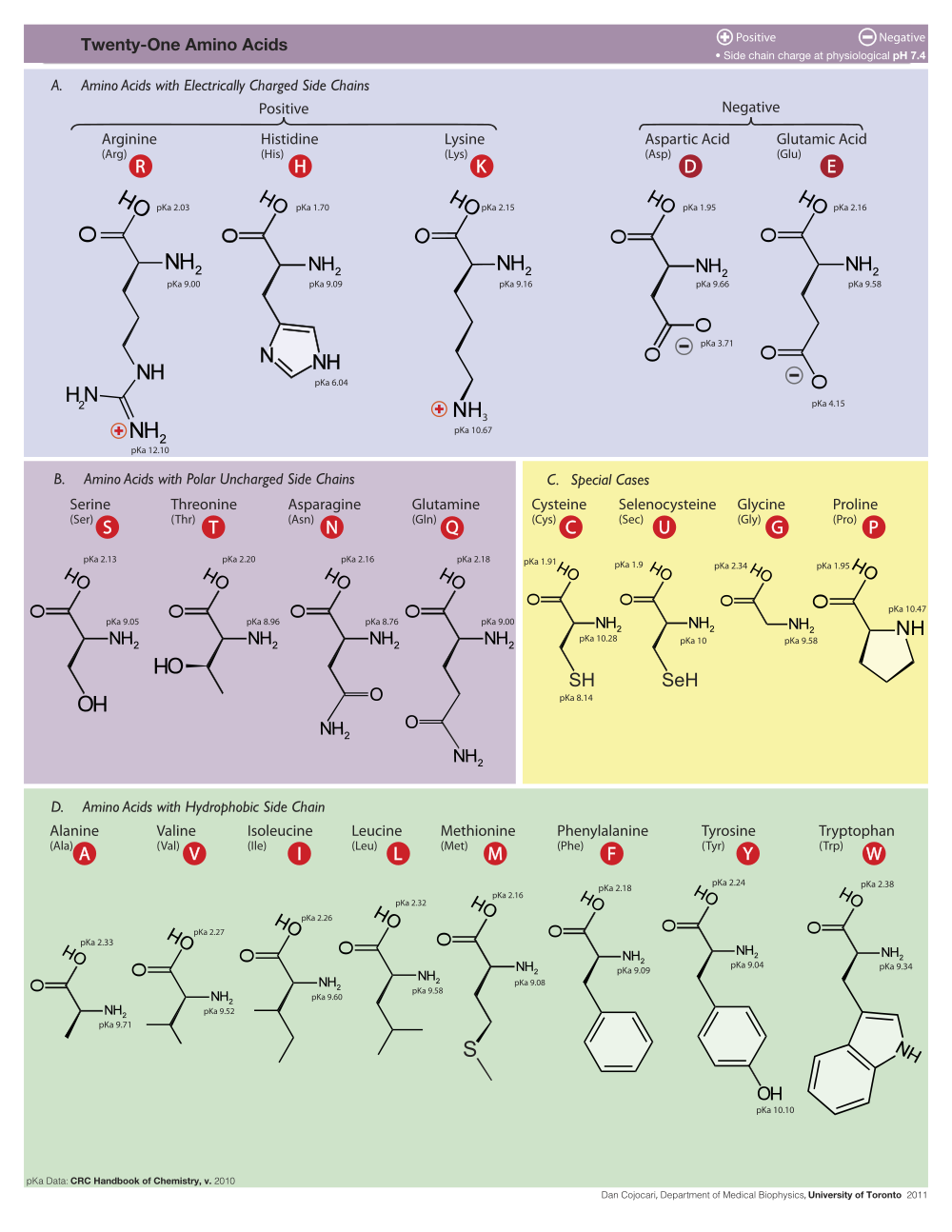
Here are the twenty standard amino acids, with their three and one-letter abbreviations. Mnemonic names may help you to remember the one-letter codes, but are not the correct names.
|
Ala A Alanine
Arg R Arginine Asn N Asparagine Asp D Aspartic acid (mnemonic: asparDic) Cys C Cysteine |
Leu L Leucine
Lys K Lysine (mnemonic: liKesine) Met M Methionine Phe F Phenylalanine (mnemonic: Fenylalanine) Pro P Proline |
mnemonic:
A Ala B Asx† C Cys D Asp asparDic E Glu gluEtamine F Phe Fenylalanine G Gly H His I Ile J K Lys liKesine L Leu M Met |
mnemonic:
N Asn asparagiNe O Pyl* P Pro Q Gln Quetamine R Arg aRginine S Ser T Thr U Sec* V Val W Trp tWptophan X Unk† Y Tyr tYrosine Z Glx† |
|
Gln Q Glutamine (mnemonic: Quetamine) Glu E Glutamic acid (mnemonic: gluEtamic) Gly G Glycine His H Histidine Ile I Isoleucine |
Ser S Serine
Thr T Threonine Trp W Tryptophan (mnemonic: tWyptophan) Tyr Y Tyrosine Val V Valine |
||
† Asx: Asn or Asp; Glx: Gln or Glu; Unk: unknown. IUPAC/IUB 1971 publication defining one-letter codes. | |||
In brief, Ligands+ means everything in the model that is not a chain of protein or nucleic acid or water. Thus, Ligands+ includes substrate or inhibitors, prosthetic groups such as heme, cofactors such as NAD, carbohydrate, metal ions, and so forth, regardless of whether these are covalently or non-covalently bound to the protein or nucleic acid chains. It also includes isolated standard amino acids or nucleotides that are not members of a standard protein or nucleic acid chain. See also the help that appears when you toggle the Ligands+ button on (in the Tab).
In the initial view, Ligands+ are spacefilled, making them stand out on the cartoon view. The spacefilled Ligands+ can be toggled on/off with the Ligands+ button (in the Tab). Non-standard amino acids or nucleotides that are part of a protein or nucleic acid chain are not spacefilled in the initial scene, but are marked with an "X" on the cartoon view. They can be rendered as ball-and-stick with a checkbox in the lower panel that appears when you toggle on the Ligands+ button (in the Tab).
More technically, Ligands+ are defined as including two subsets of atoms:
- Subset 1
is selected with not (protein,nucleic,water), where
protein is defined as Jmol's term "protein",
plus the 20 standard amino acids. (Earlier versions of Jmol occasionally failed
to identify some amino acids as protein.)
[More..]
This subset includes substrate or inhibitors, prosthetic groups such as heme, cofactors such as NAD, carbohydrate, metal ions, and so forth, regardless of whether these are covalently or non-covalently bound to the protein or nucleic acid chains. Examples are cadmium in 1D66, heme (HEM) in 2HHD, glycosylation of the protein in 1IGT, and detergent (OCT) and phosphorylation (PHO) of serine and threonine in 1APM.
- Subset 2 includes standard amino acids or nucleotides that are not
part of a polymer chain (isolated single residues,
single residue "chains") or that lack certain standard atoms.
If not included in Ligands+, these would be invisible in
displays such as Cartoon, Secondary Structure, N->C Rainbow, and Vines with
sidechains hidden.
[More..]
Examples include GLY308 in 4CPA, and A351 in 1BKX.
See also anomalous atoms.
DNA and RNA are defined within Jmol. No errors in these definitions have been noticed.
Protein is defined within Jmol, but the definition in former versions was flawed. Rarely, some standard amino acids failed to be included (examples). Therefore, FirstGlance defines protein as:
The above definition is probably unnecessary in the current version of Jmol, but since it isn't broken, it hasn't been "fixed". Using the Jmol-defined term "protein" includes some non-standard amino acids, as intended (see next section below).
Carbohydrate is defined current Jmol as a list of residue ID's that occur in the PDB. This list probably needs more regular updating. In particular, when checked in April, 2013, it lacked Allose [ALL], present in the single PDB entry 1rpj. Currently, FirstGlance defines 'carbohydrate' as follows:
View Options. Initially, non-standard residues are labeled X, and the number present is reported in the introductory help panel (unless there are none). These labels can be controlled with the labels checkboxes. Also, the non-standard residues can be shown as balls and sticks, using a checkbox in the Help panel for Ligands+, or under Advanced/Technical which is in the Tools tab.
Definitions. Standard amino acids and nucleotides are defined in the Protein Data Bank file format (PDB format), and have record type ATOM. These include:
- The 20 standard amino acids, plus ambiguous residue codes ASX, GLX, and undetermined UNK.
- Twelve standard nucleotides A, C, G, I, T, U, DA, DC, DG, DI, DT, and DU plus UNK.
-
The distinction between ribonucleotides (A, C, G, I, T, U) and
deoxyribonucleotides (DA, DC, DG, DI, DT, DU) was first made when
the PDB was
remediated
on August 1, 2007.
Backbone Traces. Non-standard amino acids and nucleotides, or the non-standard atoms within them, have record type HETATM. Regardless of whether the standard main-chain atoms within a residue are ATOM or HETATM, Jmol usually deems these residues "protein", "DNA", or "RNA" and includes them in backbone traces.
Distinguishing Non-Standard Residues. When FirstGlance in Jmol is asked to highlight non-standard residues (with the checkboxes in the help panels for Ligands+ or Advanced/Technical..) (in the Tools tab), it does so by selecting "hetero and (protein, nucleic)".
- This method works correctly only when all atoms (notably including the standard
main-chain atoms) in non-standard residues
are deemed HETATM in the PDB file.
Examples include the many non-standard nucleotides in the t-RNA
1EVV
(2MG, H2U, M2G, OMC, OMG, YG, PSU, 5MC, 5MU, 7MG, and 1MA),
the non-standard seleno-methionines in
1H3O,
and the non-standard phosphorylated serines and threonines in
1BKX.
Typically, in these cases, the entire non-standard HETATM residue
is given a non-standard PDB residue code name, such as
MSE for selenomethionine, SEP for phosphoserine, or TPO for phosphothreonine.
The corresponding full
names can be seen in the
MODRES or HETNAM records in the PDB file header (available
from pdb.org,
e.g. Header
of 1EVV), or by clicking the PDB or OCA links in control panel (upper
left) of FirstGlance.
- This method fails when an alternative convention
is used in the PDB file: designating the standard main-chain atoms
within a non-standard residue as ATOM, and only the non-standard atoms
as HETATM. An example is
GLY5 with PYL1005 in
1B07.
In such cases, FirstGlance
displays the non-standard portions of these residues as
"Ligands+". (Many earlier such cases were fixed in
remediations. For example, SER or THR plus PHO became SEP or TPO in remediated
1APM.)
Sidechain atoms (other than hydrogens) may be missing from some residues. Residues with missing sidechain atoms (C, N, O, S) are marked S- (see Labels). Typically, the atoms farthest from the alpha carbon (or the nucleotide pentose) may be omitted from the model due to local disorder (low resolution) in the electron density map. Examples include 1BL8 and 1APM.
In the Charge.. display, there is an option to color charged atoms only. Since these are at the ends of sidechains, farthest from the main chain alpha-carbon atoms, they are sometimes missing, and cannot be colored. Light colors are applied to all atoms present in such residues (in addition to S- labels) are used to indicate where this occurs.
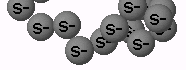
|
| Appearance of a protein model that contains only alpha-carbon atoms (1A1D). |
Methods: In each standard residue, one or two atoms farthest from the alpha carbon (or phosphorus atom in nucleotides) are checked. If any of these atoms are missing, the alpha carbon (or phosphorus) is labeled S-. The list of atoms checked is in this spreadsheet (MS Excel format): sidechain_termini.xls. The script that selects residues with incomplete sidechains is in the file scripts.js, in makeDefineIncompleteSidechainsSpt().
Atoms missing in non-standard residues or ligands will not be reported.
If a standard residue contains some atoms, but lacks the alpha carbon or phosphorus atom, the S- label will fail to be displayed.
Resolution is graded arbitrarily as follows. If you have suggestions for improving this grading scheme, please contact
| Resolution, Å | Grade |
| <1.6 | EXCELLENT |
| 1.6 - 1.79 | EXCELLENT/VERY GOOD |
| 1.8 - 1.99 | VERY GOOD |
| 2.0 - 2.29 | VERY GOOD/GOOD |
| 2.3 - 2.59 | GOOD |
| 2.6 - 2.89 | GOOD/FAIR |
| 2.9 - 3.19 | FAIR |
| 3.2 - 3.49 | FAIR/POOR |
| 3.5 or greater | POOR |
| Resolution | Free R | ||
| GoodQ | Median | BadQ | |
A table representing the distributions of free R values for a range of resolutions was constructed. At each resolution, the table gives the median free R, as well as the boundaries for the lower quartile (GoodQ) and the upper quartile (BadQ). For resolutions 1.0 - 3.5, these values were obtained from Figure 3C in Read et al., 2011, A new generation of crystallographic validation tools for the protein data bank. For resolution 4.0, the values were obtained using Advanced Search at RCSB.Org.
Free R values are graded by FirstGlance in Jmol using this method. The resolution is rounded to the nearest tenth, and the corresponding free R values are looked up in the table and used as follows. (Resolutions between 3.5 and 4.0 were rounded to the closest of those two values. This was considered acceptable since the Free R values for those two resolutions are very close to each other.) The values 0.02 were chosen arbitrarily while inspecting Figure 3C.
| Free R Value | Grade | |
| <= (GoodQ - 0.02) | MUCH BETTER THAN AVERAGE at this resolution | |
| ------ GoodQ (best 25%) | > (GoodQ - 0.02) and <= ((GoodQ + Median)/2) | BETTER THAN AVERAGE at this resolution |
| ------ Median | > ((GoodQ + Median)/2) and <= ((Median + BadQ)/2) | AVERAGE at this resolution |
| ------ BadQ (worst 25%) | > ((Median + BadQ)/2) and <= (BadQ + 0.02) | WORSE THAN AVERAGE at this resolution |
| > (BadQ + 0.02) | UNRELIABLE | |
You can enter any atom expression, from Jmol's into the Find.. slot. Examples:
- rna (all RNA)
- g, c (guanidylate and cytidylate in either DNA or RNA)
- da, dt (adenylate and thymidylate in DNA; see standard residues)
- (g,c) and rna (guanylate and cytidylate in RNA)
- (a, t) and *.c5' (one atom per nucleotide). C5' is present in both ribose and deoxyribose.
- (a, t) and phosphorus (nucleic acid backbone phosphorus atoms). Note that the 3' (hydroxy) terminal nucleotides have no phosphorus.
- gly.ca (carbon-alpha in glycine)
- met.sd (sulfur-delta in methionine)
- mse (the group name for selenomethionine, e.g. in 1K28)
- sulfur (all sulfur atoms; use full names for elements)
- 12-23 (all residues/groups with sequence numbers in this range)
- 12-23:b (residues/groups in chain B with sequence numbers in this range)
- 12-23 and protein (excludes non-protein, such as water or DNA)
- 12-23 and nucleic (excludes non-nucleic, such as water or protein)
The syntax sequence=acde is not a Jmol atom expression. That syntax, when entered into Find.., is translated by FirstGlance into Jmol syntax (within('acde', all)). The Jmol syntax is displayed in gray text at the very bottom of the Find..'s help panel.
Note that "atoms with halos" (from Find..) can be designated as a target for the Contacts.. tool (see the checkbox for this purpose in Contacts..). That is, you can visualize atoms non-covalently interacting with the "atoms with halos". Thus, Find.. can be used to select target atoms that are problematic to select with the target selection options in the Contacts.. interface.
"Atoms with halos" can also be hidden or isolated (see Hide.. and Isolate.. near the bottom of any tab except Preferences.
The following procedure may be used to calculate the isoelectric pH (pI) of a protein chain, and the net charge of the chain at various pH values:
- If your PDB file contains multiple protein chains, decide which chain you are going to analyze for pI and charge.
- Decide whether you want
- The values for the protein used in the experiment (crystallized or for solution NMR), which is often a fragment of the full-length protein, or
- The values for the full-length protein chain.
To find out how much of the full length chain was deleted for the experiment, follow these instructions.
-
Obtain the one-letter sequence of the protein chain by clicking
the Sequences link in the molecule tab (the tab labeled with
the PDB code).
- Experimental fragment: use the OCA link.
- Full-length protein chain: use the UniProt link.
- Copy the sequence and paste it into the large box at the Protein Calculator.
- Check the three boxes under Charge at the right, and click Submit.
Other servers that calculate protein charge are listed in the Wikipedia article on Protein pKa calculations. pKa values for amino acids are given in the Wikipedia article Proteinogenic amino acid.
- What are "atoms with halos"? Use the Find..
link (in any tab except Preferences) to apply halos to atoms that you specify.
Halos are bright yellow (see snapshots at right -- touch snapshots
with your mouse for more information).
- Why aren't all residues in the chain selected?
Non-standard residues (if any are present) are not selected when
you click on a chain -- only the standard residues are selected.
(Non-standard residues are colored slightly darker than the
standard residues, but the same hue as the rest of the chain. You
can highlight non-standard residues with a checkbox under
Ligands+ or under Advanced/Technical in the Tools tab.)
This has the advantage that
you see the contacts between the standard residues (target) and
the non-standard residues. If you wish to add the
non-standard residues to the target, there are two methods.
- If there are only a few, change the selection mode to
Residues/Groups and click on each of them.
- If there are many of them, use Find.. to put halos around the desired target. For example, you could enter a particular chain (prefix the chain name with a colon, such as :A for chain A), or protein, dna, or rna. (Even the non-standard residues will have halos.) Then enter Contacts.. and check Atoms with Halos. Next, Show Atoms Contacting Target. At this point, you can click Find.. and clear the halos, and then return to contacts (using the Return to Contacts link at the top of the lower left panel).
-
Examples:
- 1BKX has two non-standard residues in protein chain A.
- 1EVV, a tRNA, has many non-standard residues.
- If there are only a few, change the selection mode to
Residues/Groups and click on each of them.
- Why can't I deselect by clicking on something already selected?
In general, when you selected something by clicking on it, you can deselect it
with a second click. For example, if the selection mode is "Chains"
and you have already selected Chain A, clicking on Chain A again
will deselect it. However, when you are clicking on something
that is included in a larger selected set of atoms, it will not
be deselected. For example:
- If Chain C is selected, and then you change the selection mode to
"Residues/Groups", clicking on a residue in chain C will not deselect that
one residue.
Solution:
To select large portions of a chain, use the "Range of residues in one chain"
mode.
- If you have selected "Atoms with Halos", and the selection mode is "Residues/Groups", you cannot deselect atoms with halos by clicking on those atoms. Solution: Uncheck "Atoms with Halos". Now, with the selection mode set to "Residues/Groups", use the halos as a guide to click on the subset of groups with halos that you want.
- If Chain C is selected, and then you change the selection mode to
"Residues/Groups", clicking on a residue in chain C will not deselect that
one residue.
Solution:
To select large portions of a chain, use the "Range of residues in one chain"
mode.
- How do I use sequence numbers to target a range of residues? Suppose you want to target the range of sequence numbers 22-33. In the Find.. dialog, enter "22-33" to put halos around the 12 residues from 22 through 33. Now click Contacts... There, check Target Atoms with Halos. Now you are ready to Show Atoms Contacting Target. If there is more than one chain with residues 22-33, append a colon followed by the chain name you want. For chain B, enter "22-33:b" in Find...

The mechanism used to select unnamed chains is detailed in Technical Information.
The Contacts.. dialog in FirstGlance shows atoms likely to be noncovalently (or covalently) bonded to any target set of atoms that you select. Such atoms are deemed "contacts", and are shown as spheres (either of van der Waals radii, or of smaller radii in "ball and stick" rendering). "Contacting" atoms are determined solely by distance from the target, using the following criteria. Suggestions for improving the following criteria are welcome (see feedback address at the bottom of this document).
FirstGlance shows only the proximal atom pairs, leaving it to the viewer to judge whether a non-covalent bond actually exists between them. (Jmol has well-developed code for showing hydrogen bonds as bond sticks, but FirstGlance does not yet use this capability of Jmol. For details, see the hbonds command in the
- Putative hydrogen bonds:
nitrogen or oxygen atoms that are within
3.5 Å of nitrogen or oxygen atoms within the target.
Protein hydrogen bonds with donor-acceptor
distances of less than 3.2 Å are energetically significant. When
donor-acceptor distances exceed
3.5 Å, the bond energy falls to questionable significance.
More
about hydrogen bonds.
A hydrogen bond between
a donor-acceptor pair within 3.5 Å requires the presence of
a hydrogen atom between the donor and acceptor, and suitable angles
between the donor proton and the lone electron pair on the acceptor.
Examination of hydrogen atom positions is quite
helpful. Nevertheless, what appear to be energetically significant
hydrogen bonds may not meet stringent angular criteria
(Morozov
et al., 2004;
see example below).
- Simple example of hydrogen bonds:
Either protein chain in 1D66 recognizes the DNA sequence
CGG through hydrogen bonds.
-
Hydrogens can be added to PDB files lacking them by
the MolProbity server (see link under Key Resources).
After saving the resulting model to disk,
it can be uploaded for examination in
firstglance.jmol.org.
Be cautious, however, because the accuracy of
donor-acceptor distances and angles depends on the
resolution
and
local disorder. Be sure to examine your structure
with Local Uncertainty under the Views tab.
- Example of non-bonds: What appear to be hydrogen bonds in the "dry interface" in the amyloid-like fiber structure reported by Nelson et al. (2005) (see Figures rendered in Jmol) were determined not to be such after careful examination of the angles (David Eisenberg, personal communication).
- Simple example of hydrogen bonds:
Either protein chain in 1D66 recognizes the DNA sequence
CGG through hydrogen bonds.
- Water and water bridges.
In the Contacts Shown display, hydrogen bonds in which one partner is water can be displayed separately from hydrogen bonds in which neither partner is water. Water bridge in 1D66 between the sidechain nitrogen of Arg 46
(chain B)
and the phosphate in Cytosine 13 (chain D).
Water bridge in 1D66 between the sidechain nitrogen of Arg 46
(chain B)
and the phosphate in Cytosine 13 (chain D).
Furthermore, water bridges can be shown separately (a subset of hydrogen bonds involving water). Each bridge includes at least these three atoms:- A target oxygen or nitrogen within 3.5 Å of a non-target water oxygen.
- The bridging non-target water oxygen.
- A non-target, non-water oxygen or nitrogen within 3.5 Å of the bridging water.
Examples:- In 1D66 (Gal4 bound to DNA), protein chain A has a single water bridge, going to DNA. DNA chain D has four water bridges to DNA chain E.
- In 1BL8, the potassium channel, target any chain in Contacts.. and display only the water bridges. There is a single water in the channel which bridges the four chains. (There are also nice cation-pi interactions between chains.)
- In 1LCD, numerous waters with hydrogens bridge the protein to the DNA.
- Van der Waals interactions.
Carbons, sulfurs, or seleniums within 4.0 Å (see Note* below) of
carbons, sulfurs, or seleniums
within the target. These are sufficiently close for energetically
significant van der Waals "hydrophobic" interactions, and include
C-C (including aromatic ring-stacking), C-S, C-Se, and S-S interactions
(including disulfide bonds between target and contacting atoms, for
example, between the two heavy chains in antibody
1IGT).
- The two chains of 1D66 contact each other forming a small, buried, hydrophobic core.
- The ring stacking contacts to any deoxynucleotide base in the DNA in 1D66.
- The contacts to heme (HEM) in 2HHD.
- *Note: The distance cutoff was 4.5 Å until version 1.46 of FirstGlance in Jmol (released June 17, 2012). Several crystallographers recommended that this distance be reduced to 4.0 Å.
Simple examples of hydrophobic interactions:
- Salt bridges:
Sidechain nitrogens with a full electronic positive charge at neutral pH
(arg.ne,arg.nh?,lys.nz)
within 4.0 Å of sidechain oxygens with a full electronic
negative charge at neutral pH
(asp.od?,glu.oe?).
More about salt bridges.
There are two ways to visualize protein salt bridges in FirstGlance: (i) Contacts.. shows them between a target you select and the remainder of the model; (ii) Salt Bridges/Cation-Pi.. (in the Tools tab) enables you to find them throughout the model. Salt bridges where one or both partners is not a standard amino acid are not shown in these views.- Example: Each chain in 2HHD has one salt bridge in each direction between chains A and C.
- Cation-pi interactions:
Cationic sidechain nitrogens (lysine or arginine)
within 6.0 Å of the face of an
aromatic ring (phenylalanine, tyrosine, or tryptophan) may engage in
polar interactions called "cation pi interactions"
(Gallivan
& Dougherty, 1999).
For a brief introduction, see
More about cation-pi interactions.
There are two ways to visualize cation-pi interactions in FirstGlance: (i) Contacts.. shows them between a target you select and the remainder of the model; (ii) Salt Bridges/Cation-Pi.. enables you to find them throughout the model. Cation-pi interactions where one or both partners is not a standard amino acid are not shown in these views.- FirstGlance displays possible cation-pi interactions based on the
cation being within 6.0 Å of three alternate carbons in an aromatic
ring. FirstGlance will fail to show some
energetically significant cation-pi interactions,
and some that it shows will not be energetically significant.
Please see the
CaPTURE server
for a reliable listing of cation-pi interactions
in any PDB file.
Occasionally, FirstGlance will show lysine or arginine without a contacting ring (a bug). FirstGlance's present routines look for three ring atoms within 6.0 Å, but cannot tell if the three are in the same ring. An example is 2HHD, where ARG141 in chains A and C are displayed without ring partners. This is because both TYR35 and TRP37 have ring atoms within 6.0 Å, but neither ring has three such atoms. CaPTURE deems the interaction with TRP37 to be energetically significant, despite its failing the 6.0 Å rule.
- Neither FirstGlance nor CaPTURE will report cation-pi interactions
where the cation or aromatic ring are not standard amino acid components.
Examples include metal cations, or aromatic rings in ligands.
FirstGlance can, however, show the contacts for any moiety, so you
could select metals or ligand aromatic rings, and visualize their
contacts.
-
Examples:
- One end of peptide chain P in 2VAB contains PHE1:P interacting, in an energetically significant manner according to CaPTURE, with LYS66:A.
- Each chain in the homotetramer 1BL8 has one cation-pi interaction with each of the two chains it contacts. These are deemed energetically significant by CaPTURE.
- The peptide chain C has one energetically significant cation-pi interaction with chain A in 1B07.
- Firstglance finds two LYS:PHE cation-pi interactions, one in each direction, between chains B and D in 1IGT. CaPTURE is unable to handle PDB files that contain "inserted" sequence numbers, and this includes 1IGT. However, if the PDB file is renumbered (with RasMol) and saved, then uploaded to CaPTURE, results are obtained. CaPTURE deems neither of the proximities detected by FirstGlance as energetically significant.
- FirstGlance displays possible cation-pi interactions based on the
cation being within 6.0 Å of three alternate carbons in an aromatic
ring. FirstGlance will fail to show some
energetically significant cation-pi interactions,
and some that it shows will not be energetically significant.
Please see the
CaPTURE server
for a reliable listing of cation-pi interactions
in any PDB file.
- Metal and miscellaneous bonds
include three categories of distance-based atom pairs.
- Sulfur atoms within 3.2 Å of a metal atom
(presumed to be a cation). "Metal" is defined as
any metal that occured in the Protein Data
Bank in April, 2013 (orignal list was from April, 2006),
which include the following:
- francium
- Alkaline earths: radium
- Transition metals: niobium
- Lanthanides: neodymium, promethium, dysprosium, thulium
- Actinides: actinium, thorium, protactinium, neptunium, plutonium, americium
- Any atom outside the target
that is not (carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, or hydrogen) within
3.5 Å of any atom within the target that is not
(carbon, sulfur, or hydrogen); and vice versa. Atoms deemed to be involved in
putative hydrogen bonds (see above) are then excluded.
The resulting set includes, for example, O-metal, Se-metal,
and metal-to-metal interactions, as well as chloride ion
interactions with polar moieties, but excludes metal ions interacting
with sulfurs.
- Any atom outside the target
that is not (carbon, sulfur, phosphorus, or hydrogen) within
3.5 Å of any metal atom within the target;
and vice versa. This finds atoms such as nitrogen or oxygen
that are probably bound to metals, regardless of whether they may
also appear to be involved in hydrogen bonds.
The resulting set includes, for example, the sidechain nitrogen
in HIS bound to Fe++ in heme.
- Any atom outside the target that is not (carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, or hydrogen) within 4.5 Å of any atom in the target, or vice versa. This includes, for example, metal or chloride ions interacting with any element, and Se-C or Se-S interactions. This rule is also intended to display interacting elements not anticipated by the preceding rules.
- Examples (using Contacts..):
- Targeting either a protein chain in hemoglobin 2HHD, or a heme group, or an iron atom in a heme, shows the histidine sidechain nitrogen interacting with the Fe++.
- Targeting either one cadmium atom or one protein chain in 1D66 reveals the cadmium-sulfur bonds, and the cadmium-cadmium proximity.
- Targeting the three potassium ions in 1BL8 reveals their bonds to nearby oxygens.
- Targeting the three potassium ions in 1KF1 reveals their anhydrous bonds to DNA oxygens.
- 1IXJ includes DNA,
water, CoN6H18 (cobalt hexamine) and
MgO6H12 (magnesium hexahydrate).
- Sulfur atoms within 3.2 Å of a metal atom
(presumed to be a cation). "Metal" is defined as
any metal that occured in the Protein Data
Bank in April, 2013 (orignal list was from April, 2006),
which include the following:
Hydrogen is often absent in crystallographic models, because it is usually not resolved by X-ray diffraction. In contrast, hydrogen is typically present in NMR results. In some crystallographic models, hydrogens have been added by molecular modeling, either to polar atoms only, or to all atoms.
Here is More about Hydrogen.
- Hydrogen in Contacts Shown:
In the "Contacts Shown" display, only those hydrogens bonded to
contacting atoms (balls) are shown. (Hydrogens bonded to non-contacting atoms [sticks]
are not shown.) Hydrogens are shown as sticks connected to balls to make
the angles of these bonds clear.
- Example: Select the single sodium ion in 1LCD as target, and show its contacts. The hydrogens on the waters contacting the Na+ ion point away from it, consistent with the metal ion binding to lone electron pairs of the water oxygens.
Label Contacts is superceded by checking Sequence Numbers or Residue Names. Uncheck these to enable Label Contacts.
A label is shown for each amino acid or nucleotide (including non-standard residues) that contains any contacting atoms. (Labels are not shown for contacting ligands or solvent. Click on these to identify them.) Labels are in this format:
I. Alerted according to preference.
The Preferences tab has a checkbox to "Report unusual components or features". When checked (true by default), you will be ALERTED when the model contains any components or features in the list below.
- An ALERT is a message that appears in a pop-up box and must be acknowledged before anything else can be done.
-
 appears below the molecule when any of the Unusual components or features
listed below are present.
appears below the molecule when any of the Unusual components or features
listed below are present.
- Under Find:, terms beginning "~" (tilde) are defined by FirstGlance. They are not built into Jmol.
Clicking on the
 halos
ALL UNUSUAL components or features
in the list below.
(Or enter ~all_unusual in the Find slot.)
halos
ALL UNUSUAL components or features
in the list below.
(Or enter ~all_unusual in the Find slot.)
- D amino acids. Examples: 2soc, 1al4. Find: ~d_aas
- Ribothymidine. Example: 5MU in 1evv. Find: T and RNA
- Deoxyribouridine. Example: DU in 1g22. Find: U and DNA
- GLX or ASX (ambiguous) residues. Example: 1kp0. Find: GLX or ASX
- Unknown atoms X. Example: 1kp0. Find: *.x??
- Unknown atoms or groups UNX or UNK. Examples: 5wbn, 5g4a, both in 3hm6. Find: UNX or UNK
- Unknown nucleotides "N". Examples: in polymer chain, 2i82; not in polymer, 3dzi. Find: [n]
- Unknown ligands "UNL". Examples: 6eqq, Find: UNL
- Anomalous atoms. Example: none known.
Find: ~anomalous_atoms
- Amino acids lacking alpha carbon atoms. Example: Thr918 in 1h3o, and Lys214 in 2fd8 have only a nitrogen atom. Find: ~nobackbone_aas
- Amino acids lacking peptide-bonding atoms. Example: Gln8 in 4en3. is missing a main chain nitrogen atom. Find: ~unbondable_aas
- Amino acids lacking main chain oxygens. Examples: Gly5 in 1b07; Met79 in chain M in 1uc5. Find: ~nomainchaino_aas
- Single amino acid, not part of a polymer. Example: Gly308 in
4cpa.
Find: ~unchained_aas
- Single nucleoSide (no phosphate), not part of a polymer of standard nucleotides. Example: A351 in 1bkx. Find: ~unchained_nucleosides
- Single nucleoTide (has phosphate), not part of a polymer of standard nucleotides.
Examples:
- Adenosine monophosphate (AMP) phosphodiester-bonded to 7BV in 5gyz.
- Adenosine monophosphate (AMP) bound to Zinc in 5gz5.
- Adenosine 5' monophosphate (AMP) non-covalently bound to protein in 5udt.
- Adenosine 2' monophosphate (the common form is 5' phosphorylated) in 5udt.
- Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) bound to Mg in 6b8b.
- Adenosine diphosphate (ADP) non-covalently bound to protein in 6bLb.
- Adenosine 5'-triphosphate (ATP) in 5g4a.
- Guanosine di- and tri-phosphate (GDP, GTP) non-covalently bound to protein and Mg in 5nd4.
- Cyclic nucleotides. Examples:
- Cyclic-AMP (CMP) non-covalently bound to protein in 5kjx.
- Cyclic-GMP (PCG) non-covalently bound to protein in 5c8w.
- 2',3'-cyclic AMP (ACK) in 2ype.
- Insertion codes (see Unusual sequence numbering). Example: 1igy. Find (^ means the following character is an insertion code; "?" means any insertion code): ^?
- Zero or negative sequence numbers. Examples: 1d5t, and see others in Unusual sequence numbering. Find: resno < 1
Cases with multiple unusual components or features include 4cpa, 5v0g, 1h3o.
II. Alerted unconditionally.
The following rare circumstances are ALERTED unconditionally (regardless of the preference setting):
- When protein is modeled with only alpha carbon atoms, or nucleic acid chains are
modeled with only backbone phosphorus atoms. Examples:
protein in
1a1d,
protein and DNA in
1bdx.
Find: click on
 below the molecule.
below the molecule.
- When missing residues are not marked with empty baskets because nearby residues with coordinates (upon which to "hang" the empty baskts) were not found. Example: 4o46.
- When the number of models given in the NUMMDL record does not agree with the number of conformers submitted in REMARK 210. Example: 2j15.
- When there are multiple models with alternate locations. Example: none known.
III. Listed but not alerted.
The following more common features are NOT ALERTED. They are all reported routinely in the Molecule Information Tab when they occur. (An ALERT is a message that appears in a pop-up box and must be acknowledged before anything else can be done.)
- Missing residues. Count reported in the Introduction and in the Molecule Information Tab, where a link reports the missing sequence numbers in each chain. Example: 1d66. Find: cannot be found since they are absent in the model. Indicated in FirstGlance by "empty baskets".
- Incomplete (Missing) sidechains. Count reported in theIntroduction and in the Molecule Information Tab. Labeled with S- in the molecular display. Example: 2ace. Find alpha carbons: ~incomplete_sidechains. Find all atoms in residues with incomplete sidechains: within(group, ~incomplete_sidechains).
- Unusual chemical elements are reported in boldface in the Molecule Information Tab under the atom count, with a link that reports counts of atoms of each chemical element present. Example: 1ihu. Find: click on the element count in the Molecule Information Tab to display Chemical Elements with counts. Click on an element to find it.
- The count of atoms with alternate locations is given in the Molecule Information Tab under the atom count, with a link that provides an explanation and a link to Find alternate locations. Example: 1bsz.
- Non-standard amino acids or nucleotides are listed in the Molecule Information Tab along with the count of each. Examples: protein, 3c1p; RNA, 1evv. Find: Each is clickable in the listing.
Anomalous atoms no longer occur in models obtained from the PDB, to the best of our knowledge, since 2010. Their absence results from improvements in Jmol and remediations of the PDB. The information below, and the code in FirstGlance for handling anomalous atoms, remain available primarily in case anomalous atoms should occur in PDB files obtained from sources other than the PDB.
Definition. Atoms that are not recognized by Jmol as being one of: protein, nucleic acid, or "hetero".
Rationale: According to the rules for PDB files, all atoms that are not members of standard residues in protein or nucleic acid chains should be designated "hetero". Hetero atoms are typically further subdivided: there is "solvent" (water and some inorganic anions such as sulfate and phosphate), and everything else is "ligand". Rare PDB files don't follow the rules, and these confuse Jmol. And rarely, Jmol may interpret PDB files incorrectly. The result is atoms that are neither protein, nucleic acid, nor hetero. Within FirstGlance, these are deemed anomalous atoms.
 Problem. FirstGlance will often fail to display
anomalous atoms appropriately. Some anomalous atoms could be invisible
in all views except Vines (with details on).
Problem. FirstGlance will often fail to display
anomalous atoms appropriately. Some anomalous atoms could be invisible
in all views except Vines (with details on).
Solution. In order to avoid leaving anomalous atoms invisible, they are initially always shown as dot surfaces of van der Waals radii (see snapshot at right), and labeled ?. These labels can be hidden, brought to the front, or expanded into full identifications with the Labels Checkboxes.
The colors of the dots vary depending on the view. These dots are easily distinguished from halos because they are less dense, are arranged in a spherical pattern instead of a flat ring, and are usually not yellow.
Advanced/Technical.. (Tools tab) has an option to hide the dots for anomalous atoms, without hiding the labels for missing sidechains and non-standard residues.
Examples -- Odd PDB files now handled correctly
Although I know of no entries in the PDB containing atoms deemed anomalous by Jmol (in February, 2013), here are some formerly troublesome cases that FirstGlance and Jmol now handle correctly.
- THR918 in
1H3O,
and
ALA333:C in
1PRC
lack all atoms except the peptide-bonded nitrogen.
- The main chain oxygen (.O) is missing from
GLY5 in
1B07,
and MET79:M in
1UC5.
- 1GRH, in its original form,
had only two residues, CYS and EOH (ethanol), with the ethanol covalently
linked to the CYS sulfur. Formerly, CYS atoms were ATOM, and EOH was called HEC
with HETATM. After one stage of remediation, the CYS was deemed HETATM.
In the current (early 2013) remediation, the entire protein has been
added, leaving CYS 48 as ATOM and EOH as HETATM (see the end of REMARK 3).
FirstGlance shows the EOH as Ligand+.
- Entries containing D amino acids:
- 2SOC. is an octapeptide of (from SEQRES) DPN CYS PHE DTR LYS THR CYS THO.
- 1AL4: FOR0, VAL1, ILE1, GLY2, continuing (without further sequence number anomalies) ALA3 DLE ALA DVA VAL DVA TRP DLE TRP DLE TRP DLE TRP ETA17. Note that both VAL1 and ILE1 occupy the same physical position in the chain sequence. This represents sequence microheterogeneity in the protein that was crystallized. By convention, the ILE1 is not listed in SEQRES. Neither has an insertion code (column 27), but instead they are indicated to be alternate conformations (A and B in column 17; see PDB Format 3.2). FirstGlance handles this entry correctly.
Missing main chain atoms. Such cases could result from lack of electron density, or simply from errors in published PDB files.
Chrome (download from Google) is an excellent, popular, free, open-source web browser.
- Windows: Chrome performs almost as well as Firefox. Chrome is satisfactory.
- Mac: Chrome spins as well as Firefox, but rotation by mouse is jerkier.
Therefore Firefox is recommended for JSmol on Macs.
(Chrome out-performed Firefox in 2014, but changes in Chrome in 2015 impaired its operation of JSmol.)
- Java is no longer supported in Chrome beginning September 1, 2015. You must use a different browser if you wish to use Java.
See also other browsers.
Microsoft Edge® is a browser first released with Windows 10. In May, 2016: Its settings do not include a way to specify where downloads should go. They always go to the Downloads folder. It does not remember the previous window position when restarted.
-
Edge spins the molecule in JSmol almost as smoothly as Firefox, but
rotation by mouse is much jerkier in Edge.
Therefore Firefox is recommended for JSmol.
- Edge does not support Java. However, Internet Explorer is included in Windows 10, and it runs the Jmol Java applet well. Instructions for using Internet Explorer in Windows 10.
See also other browsers.
Firefox (getfirefox.com) is an excellent, popular, free, open-source web browser.
- Firefox runs JSmol (no Java) substantially faster than any other browser in both Windows and OS X. Therefore Firefox is recommended for JSmol.
- Java support was removed from Firefox in early 2017.
See also other browsers.
Internet Explorer is a web browser bundled with Microsoft Windows®. In 2014-2017, versions 8 through 11 worked well when using Java. However, JSmol (no Java) in Internet Explorer is unacceptably slower and jerkier than in other browsers. Therefore, when FirstGlance in Jmol is run without java (JSmol) in Internet Explorer, a warning appears recommending the use of Firefox. See also other browsers.
Opera (opera.com) is the least popular web browser among the top five PC browsers (<5% of page views), although it is predominant in Africa. Historically, Opera has been the least consistent as far as operating FirstGlance in Jmol. Feel free to try it but compare it with Firefox which has worked consistently well.
- JSmol (no Java): In 2015-2016, Opera ran JSmol satisfactorily in Windows. In OS X, rotation of the molecule is unacceptably slow and jerky. Therefore, Firefox is recommended for JSmol in OS X.
- Java: Opera no longer supports Java.
See also other browsers.
Safari is a web browser included in the Apple Macintosh OS X computer operating system.
- JSmol: Spinning is as smooth as in Firefox, but rotation by mouse is jerkier.
Therefore, Firefox is recommended for JSmol in OS X.
- Java: Safari supports Java in November, 2017.
See also other browsers.
SeaMonkey is an excellent, free, open-source web browser. For JSmol, it performs as well as Firefox in both Windows and OS X.
SeaMonkey supports Java as of November, 2017.See also other browsers.
The plan implemented in FirstGlance in Jmol version 2.7 is outlined here. Further complications, encountered during implementation and testing, remain to be added here. The code is in getCharges() in moltab.js, and makeChargeHelp() in help.js; and in getChainEnds() in modeldat.js and makeEndsHelp() in help2.js.
Some example PDB codes are listed in the lower left help panel when you click Ends (in the Tools tab).
Identification of chain ends is still not perfect. For example, the end of chain F in 1ucy is incorrectly identified due to a non-standard residue.
Starting with FirstGlance in Jmol Version 2.7 in early 2018, use of the Jmol_S Java applet is no longer encouraged. In late 2017, the Chrome, Firefox, Edge, and Opera browsers no longer supported Java applets, and Oracle (maker of Java) had announced plans to stop making the Java plug-in for web browsers.
However, if you use a Java-compatible browser, you can still use Java by adding the query parameter &java to the FirstGlance URL in the browser's address slot. Here are Instructions for Installing and Enabling Java for both Windows and OS X.
The Jmol Java applet (Java, Jmol_S frank at the lower right) and JSmol (JavaScript/HTML5, no Java, JSmol frank at the lower right) have identical molecular visualization features, but differ in speed and smoothness of rotation.
Using the Jmol java applet requires a support program called a Java virtual machine, also called simply Java. If you use Java, it is highly advisable to keep your java up to date, mostly for security reasons. At java.com, click the link "Do I have Java?" to find out if Java is installed and up to date.
If you are still using Mac OS 10.6 (Snow Leopard), check Apple Software Update, which delivers new versions of Java for Macs. We tested Snow Leopard through 2013 but we are no longer testing it, so if you have problems with FirstGlance in Jmol in Snow Leopard, consider upgrading your operating system.Java may be a security risk. Here are recommendations for using Java as safely as possible.
In late 2012, as Java became ever more problematic, Jmol was translated to javascript (HTML5), creating JSmol (see also JSmol in the Jmol wiki). JSmol displays the molecule in a web browser exactly like the Jmol Java applet, and has all other Jmol applet capabilities. However, no Java is needed. FirstGlance in Jmol was first released in a JSmol version in January, 2014.
The main page has an option to upload a file from your local disk, to be displayed in FirstGlance.
Security. Your data file (which must be in PDB format, but can have any filename type suffix) is transferred through the Internet unencrypted, and stored temporarily on a server at Bioinformatics and Biological Computing of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel. It is then re-transferred through the Internet to the Jmol/JSmol in your web browser. A sophisticated spy could capture your data. Institutions needing a secure method to upload proprietary data for display in FirstGlance in Jmol may install FirstGlance in Jmol within their secure intranet. Feel free to contact with any questions.
Method. Jaime Prilusky kindly provided a CGI program that accepts uploaded PDB files. You can put an upload slot to this program on your own web page by inserting the following HTML:
<form method='post' enctype='multipart/form-data'
action='http://oca.weizmann.ac.il/oca-bin/fgij'>
Upload a PDB file of your own:
<br><small>
Caution: uploading a PDB file may <b>disclose your data</b> to others.
</small><br>
<input type='file' name='file' size='50'>
<input type='submit' value='View in FirstGlance'>
</form>